-
 Large-Scale Synthesis of Carbon Dots Driven by Schiff Base Reaction at Room Temperature
Large-Scale Synthesis of Carbon Dots Driven by Schiff Base Reaction at Room Temperature -
 Monodentate Ligands in X-Cu(I)-Y Complexes - Structural Aspects
Monodentate Ligands in X-Cu(I)-Y Complexes - Structural Aspects -
![Crystal Structure of the Homopolyatomic Sulfur Cation [S<sub>20</sub>]<sup>2+</sup>](https://pub.mdpi-res.com/title_story/title_story_17386532829206.jpg?1743317607) Crystal Structure of the Homopolyatomic Sulfur Cation [S20]2+
Crystal Structure of the Homopolyatomic Sulfur Cation [S20]2+ -
 Application of Inorganic-Based Bionanomaterials as Biocompatible Scaffolds for Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering: Current Advances and Developments
Application of Inorganic-Based Bionanomaterials as Biocompatible Scaffolds for Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering: Current Advances and Developments
Journal Description
Inorganics
Inorganics
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal on inorganic chemistry published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Chemistry, Inorganic and Nuclear)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our authors say about Inorganics.
Impact Factor:
3.1 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.6 (2023)
Latest Articles
Electrical Features of Liquid Crystal Composition Doped with Cobalt Ferrite: Possible Sensing Applications
Inorganics 2025, 13(4), 107; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040107 - 28 Mar 2025
Abstract
The effects of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles on the properties of an electro-optical liquid crystal cell based on the nematic composition of 4-Cyano-4′-pentylbiphenyl (5CB) under the influence of different forms of bias voltage were studied. Detailed results were established for the application
[...] Read more.
The effects of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles on the properties of an electro-optical liquid crystal cell based on the nematic composition of 4-Cyano-4′-pentylbiphenyl (5CB) under the influence of different forms of bias voltage were studied. Detailed results were established for the application of sinusoidal voltages with various frequencies and amplitudes. At the input signal, with a frequency of 500 kHz, a resonant current increase was obtained in the electrical circuit, followed by a decrease in the current with an increase in the frequency. This indicates the formation of a consistent oscillatory circuit. The quality factor of the nanoparticle system does not depend on the amplitude of the controlled voltage. Liquid crystal cells with constant quality can be used in a number of devices and technologies, including extended sensing devices, where stable electrical properties are required.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Functional Inorganic Biomaterials for Molecular Sensing and Biomedical Applications)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Correlating the Characteristics and Catalytic Performance of Mn-Na-W-Ox/SiO2 for Oxidative Coupling of Methane
by
Hamid Reza Godini, Stefan Berendts, Rafael Kleba-Ehrhardt, Asma Tufail Shah and Oliver Görke
Inorganics 2025, 13(4), 106; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040106 - 28 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Chemical–structural characteristics of three differently synthesized research-benchmark Mn-Na-W-Ox/SiO2 catalysts for the Oxidative Coupling of Methane (OCM) were systematically studied in this research. XRD, EDX, ICP-OES, and SEM/FIB-SEM techniques, as well as Carrier Gas Hot Extraction (CGHE) and high-temperature XRD analyses,
[...] Read more.
Chemical–structural characteristics of three differently synthesized research-benchmark Mn-Na-W-Ox/SiO2 catalysts for the Oxidative Coupling of Methane (OCM) were systematically studied in this research. XRD, EDX, ICP-OES, and SEM/FIB-SEM techniques, as well as Carrier Gas Hot Extraction (CGHE) and high-temperature XRD analyses, were performed to explain the functional features of the studied catalysts, in particular, the features affecting the quantity and quality of the interactions of oxygen and methane with the catalyst surface and with other molecular and radical species. These enable tracking the potential for the oxygen activation and dynamic transformation of the solid-state chemistry on the surface and sub-surface of these Mn-Na-W-Ox/SiO2 catalysts. These catalysts were synthesized, respectively, via the sol–gel synthesis method (Cat1) and the incipient wetness impregnation of the non-structured silica support (Cat2) and structured SBA-15 silica support (Cat3), under different sets of temperatures and gas compositions. The catalysts with the homogenous distribution of active components, namely Cat1 and Cat3, showed similar trends in terms of their dynamic interaction with oxygen species. They also showed higher levels of crystallinity of the active materials and higher catalytic selectivity towards ethane and ethylene. An explanation is given as to how the structural characteristics of the catalysts on the nanometer–micrometer scale contribute to these. The gained knowledge will be crucial in the selection and treatment of the support and developing a proper synthesis approach for the ultimate goal of designing a selective OCM catalyst.
Full article
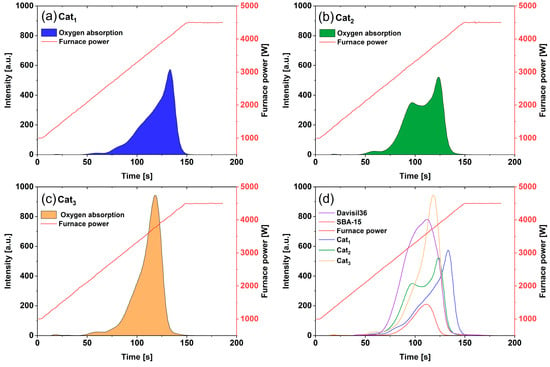
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhanced Antimicrobial and Biomedical Properties of Fe-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses Through Ag Addition
by
Long Jiang, Xueru Fan, Qiang Li, Xin Li, Tao Jiang and Qin Wei
Inorganics 2025, 13(4), 105; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040105 - 28 Mar 2025
Abstract
This study explores the enhancement of antimicrobial and biomedical properties in Fe-based bulk metallic glasses (BMGs) through the addition of Ag. Fe55-xCr20Mo5P13C7Agx (x = 0, 1, 2, 3 at.%) master alloy ingots
[...] Read more.
This study explores the enhancement of antimicrobial and biomedical properties in Fe-based bulk metallic glasses (BMGs) through the addition of Ag. Fe55-xCr20Mo5P13C7Agx (x = 0, 1, 2, 3 at.%) master alloy ingots were synthesized by the induction melting technique and industrial-grade raw materials, the master alloy ingots were prepared as bulk metallic glasses (referred to as Ag0, Ag1, Ag2, and Ag3) by the water-cooled copper-mold suction casting technique, and their glass-forming ability, corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and antimicrobial properties were systematically investigated. The results indicate that the glass forming ability (GFA) decreased with increasing Ag content, reducing the critical diameter for fully amorphous formation from 2.0 mm for Ag0 to 1.0 mm for Ag3. Electrochemical tests in Hank’s solution revealed the superior corrosion resistance of the Fe-based BMGs as compared with conventional 316 L stainless steel (316L SS) and Ti6Al4V alloy (TC4), with Ag3 demonstrating the lowest corrosion current density and the most stable passivation. Biocompatibility assessments, including fibroblast cell viability and adhesion tests, showed enhanced cellular activity and morphology on Fe-based BMG surfaces as compared with 316L SS and TC4, with minimal harmful ion release. Antimicrobial tests against E. coli and S. aureus revealed significantly improved performance with the Ag addition, achieving bacterial inhibition rates of up to 87.5% and 86.7%, respectively, attributed to Ag+-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. With their excellent corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and antimicrobial activity, the present Ag-containing Fe-based BMGs, particularly Ag3, are promising candidates for next-generation biomedical implants.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Research and Application of Amorphous Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
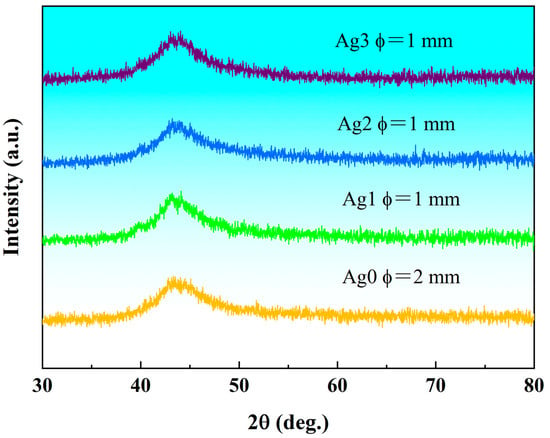
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis, Characterization, and Structural Studies of Some Homo- and Heteroleptic Cu(I) Complexes Bearing 6,6′-Bis(phenylethynyl)-2,2′-Bipyridine Ligand
by
Rayya A. Al-Balushi, Md. Serajul Haque Faizi, Md. Mushtaque, Idris J. Al-Busaidi and Muhammad S. Khan
Inorganics 2025, 13(4), 104; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040104 - 28 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Coordination-driven Cu(I) complexes constitute an interesting class of materials with rich opto-electronic properties and diverse applications. Various homo- and heteroleptic Cu(I) complexes have been reported in the literature. In continuation with our quest for new materials, we report herein two novel coordination-driven self-assembled
[...] Read more.
Coordination-driven Cu(I) complexes constitute an interesting class of materials with rich opto-electronic properties and diverse applications. Various homo- and heteroleptic Cu(I) complexes have been reported in the literature. In continuation with our quest for new materials, we report herein two novel coordination-driven self-assembled Cu(I) complexes: the homoleptic (1) and the heteroleptic (2) complexes based on the 6,6′-bis(phenylethynyl)-2,2′-bipyridine (L1) and 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline (dmph) ligands. L1 was prepared by a Pd(II)-catalyzed Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction between phenylactylene and 6,6′-dibromo-2,2′-bipyridine. Homo- and heteroleptic Cu(I) complexes were obtained by the self-assembly of L1 and dmph ligands. Complexes (1) and (2) were obtained in high yields, and are soluble in common organic solvents and stable at room temperature over a long period of time. The optical (absorption and emission) properties of both complexes were evaluated. The optical properties in solution are a function of the ligands and varied for the complexes. Complex (2) was also characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction and the intermolecular interaction was studied using Hirschfeld surface analysis. In the solid state, complex (2) exhibited four-coordinate distorted tetrahedral geometry around Cu(I). Density functional theory (B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) was utilised to determine various molecular descriptors.
Full article
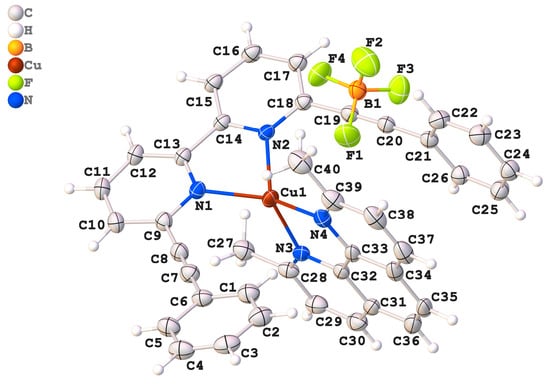
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Classification, Functions, Development and Outlook of Photoanode Block Layer for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
by
Youqing Wang, Wenxuan Wu and Peiling Ren
Inorganics 2025, 13(4), 103; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040103 - 27 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The block layer situated between the active material and electrode in photoelectrochemical devices serves as a critical component for performance enhancement. Using dye-sensitized solar cells as a representative model, this review systematically examines the strategic positioning and material selection criteria of block layers
[...] Read more.
The block layer situated between the active material and electrode in photoelectrochemical devices serves as a critical component for performance enhancement. Using dye-sensitized solar cells as a representative model, this review systematically examines the strategic positioning and material selection criteria of block layers following a concise discussion of their fundamental mechanisms. We categorize block layer architectures into three distinct configurations: single layer, doped layer, and multilayer structures. The electron generation and transport mechanisms to photoelectrodes are analyzed through structural design variations across these configurations. Through representative literature examples, we demonstrate the correlation between material properties and photoconversion efficiency, accompanied by comprehensive performance comparisons. In the single-layer section, we comparatively evaluate the merits and limitations of TiO2- and ZnO-based block layers. The doped layer discussion traces the evolutionary trajectory from single-dopant systems to co-doping strategies. For multilayer architectures, we elaborate on the flexibility of its functional regulation. Finally, we present a forward-looking perspective on the hot issues that need to be urgently addressed in photoelectrochemical device block layers.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigation on the Electron Emission Regularity of Sputtered Boron Nitride Thin Films and Microstructured Array Surfaces
by
Yuqing Gu, Juannan Li and Dan Wang
Inorganics 2025, 13(4), 102; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040102 - 26 Mar 2025
Abstract
Boron nitride (BN) ceramic is an important support material in aerospace, arc discharge devices, and vacuum electronics. The electron emission properties of BN surfaces are of significance among various space applications. In this work, by preparing BN thin films and microstructured BN bulks,
[...] Read more.
Boron nitride (BN) ceramic is an important support material in aerospace, arc discharge devices, and vacuum electronics. The electron emission properties of BN surfaces are of significance among various space applications. In this work, by preparing BN thin films and microstructured BN bulks, we have investigated the influence of the surface physical properties on the electron emission coefficient (EEC). The results showed that the surfaces of BN films, which were prepared by magnetron sputtering, produced serious gas adsorption and organic contamination when they were left for 10 days, and these surface modifications made the EEC of BN film surface decrease to a certain extent. The argon ion cleaning experiments indicated that the process of ion cleaning was able to partly eliminate the surface adsorption and contamination for the BN film. The EEC of the cleaned BN film surface was significantly improved compared to that of the original polluted BN film surface, with an EEC peak value of about 3.2 instead of 3.0 for the original polluted surfaces. By contrast, the EEC curves of the BN bulk show some difference, with the peak values of the EEC curves being 2.62 for the untreated BN bulk. The results of laser etching on the BN bulk surface to form microarray structures show that the EEC of BN bulk decreases significantly with the increase of the average aspect ratio of the microstructures. The EEC peak values of the BN bulks decrease from 2.62 to 1.16 when the porosity of the BN bulk reaches 49.11% and the aspect ratio reaches 1.36, indicating that constructing a surface microstructure is an effective method to achieve EEC reduction. By employing the electron trajectory tracking algorithm and the phenomenological model of electron emission, the effect of microstructure on EEC for BN bulk was quantitatively explained. The results of the study are of engineering application significance for vacuum devices involving the electron emission process of BN ceramic.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Boron-Based Low-Dimensional Nanoclusters and Nanomaterials)
►▼
Show Figures
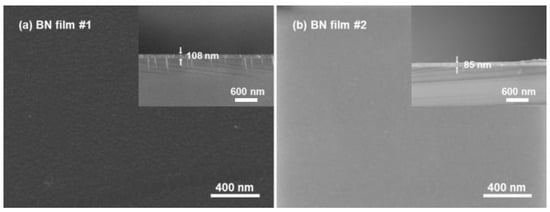
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Novel CoFe2O4@MgO@(Mg0.23Co0.77)(Mg0.35Co1.65)O4@C and CoFe2O4@MgO@C Nanocomposites for Efficient Removal of Zn(II) Ions from Aqueous Media
by
Ehab A. Abdelrahman, Reem K. Shah, Mortaga M. Abou-Krisha, Fawaz A. Saad and Abdalla M. Khedr
Inorganics 2025, 13(4), 101; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040101 - 23 Mar 2025
Abstract
Excessive levels of Zn(II) ions in aquatic environments pose significant risks to both ecosystems and human health. In aquatic systems, Zn(II) ions disrupt metabolic functions in organisms, leading to toxicity and bioaccumulation. For humans, prolonged exposure can result in gastrointestinal distress, immune system
[...] Read more.
Excessive levels of Zn(II) ions in aquatic environments pose significant risks to both ecosystems and human health. In aquatic systems, Zn(II) ions disrupt metabolic functions in organisms, leading to toxicity and bioaccumulation. For humans, prolonged exposure can result in gastrointestinal distress, immune system dysfunction, and neurological complications, necessitating effective removal strategies. This study reports the synthesis and characterization of CoFe-MgO-C-M600 (CoFe2O4@MgO@(Mg0.23Co0.77)(Mg0.35Co1.65)O4@C) and CoFe-MgO-C-M800 (CoFe2O4@MgO@C) nanocomposites for the efficient removal of Zn(II) ions from aqueous media. The nanocomposites were synthesized using the Pechini sol-gel method and characterized through X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM). XRD analysis confirmed the crystalline structure of both nanocomposites, with CoFe-MgO-C-M600 exhibiting a smaller average crystallite size (38.67 nm) than CoFe-MgO-C-M800 (75.48 nm). EDX results verified the elemental composition of the nanocomposites, ensuring the successful incorporation of key elements. FE-SEM analysis revealed significant morphological differences, with CoFe-MgO-C-M600 displaying smaller and more uniform grains compared to CoFe-MgO-C-M800. The results show that CoFe-MgO-C-M600 possesses a highly porous and interconnected structure, enhancing its surface area and adsorption potential. In contrast, CoFe-MgO-C-M800 demonstrates larger and more compact grains, which may affect its adsorption performance. HR-TEM further confirmed these findings, demonstrating that CoFe-MgO-C-M600 had a smaller average particle diameter (35.45 nm) than CoFe-MgO-C-M800 (321.14 nm). Adsorption studies indicated that CoFe-MgO-C-M600 and CoFe-MgO-C-M800 achieved maximum adsorption capacities of 276.24 and 200.00 mg/g, respectively. The adsorption process was determined to be exothermic, spontaneous, and physical in nature, following the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and the Langmuir isotherm.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Organic–Inorganic Nanocomposites for Water Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures
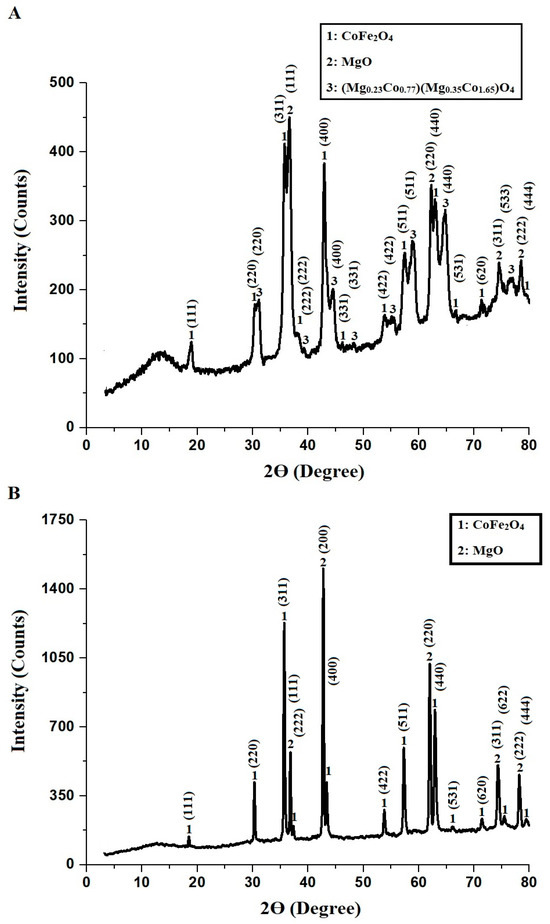
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Comparative B3PW and B3LYP Calculations of ABO3 (A = Ba, Sr, Pb, Ca; B = Sn, Ti, Zr) Neutral (001) and Polar (111) Surfaces
by
Roberts I. Eglitis, Juris Purans, Ran Jia, Sergei P. Kruchinin and Steffen Wirth
Inorganics 2025, 13(4), 100; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040100 - 23 Mar 2025
Abstract
We completed B3LYP and B3PW computations for AO- and BO2-terminated (001) as well as AO3- and B-terminated (111) surfaces of BSO, BTO, STO, PTO, CTO, BZO, SZO, and CZO perovskites. In particular, we performed the first B3LYP computations for
[...] Read more.
We completed B3LYP and B3PW computations for AO- and BO2-terminated (001) as well as AO3- and B-terminated (111) surfaces of BSO, BTO, STO, PTO, CTO, BZO, SZO, and CZO perovskites. In particular, we performed the first B3LYP computations for polar BSO (111) surfaces. We observed that most of the upper-layer atoms for AO- and BO2-terminated ABO perovskite (001) surfaces relax inward. In contrast, practically all second-layer atoms relax upward. Lastly, almost all third-layer atoms relax inward. This tendency is less pronounced for atomic relaxation of first, second, and third layer atoms for AO3- and B-terminated ABO perovskite (111) surfaces. For almost all ABO perovskites, their (001) surface rumplings s are considerably larger for AO-terminated compared to BO2-terminated surfaces. On the contrary, the ABO perovskite (001) surface energies, for both AO and BO2-terminations, are essentially equivalent. The ABO perovskite polar (111) surface energies are always substantially larger than their neutral (001) surface energies. In most cases, the surface energies of AO3-terminated ABO perovskite polar (111) surfaces are considerably larger than their B-terminated surface energies. Our computations illustrate a noticeable boost in the B-O bond covalency near the BO2-terminated (001) surface related to the bulk. Our computed ABO perovskite bulk Γ-Γ band gaps are almost always reduced near the AO- and BO2-terminated neutral (001) surfaces as well as in most cases also near the AO3- and B-terminated polar (111) surfaces.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optical and Quantum Electronics: Physics and Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
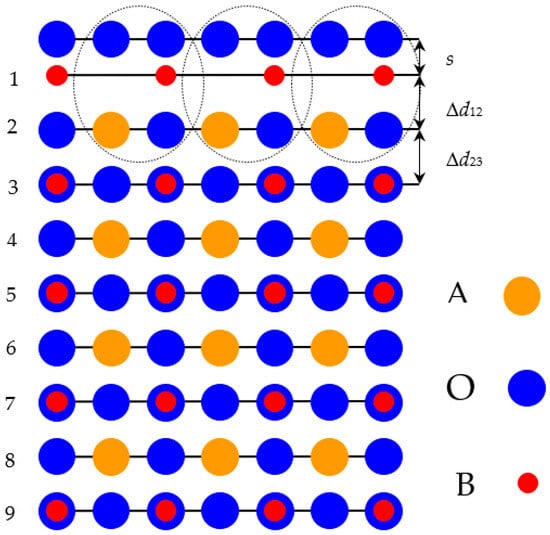
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Zn Doping on Optical Properties of Polycrystalline β-Ga2O3
by
Yue Yan, Shuai Zhu, Jing Yang, Yuanyuan Zhang, Wei Bai and Xiaodong Tang
Inorganics 2025, 13(4), 99; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040099 - 22 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this study, Zn-doped Ga2O3 polycrystalline samples were prepared by solid-phase sintering, and the effects of Zn doping on the optical properties of Ga2O3 were investigated. It is found that the introduced Zn ions disrupted the Ga-O
[...] Read more.
In this study, Zn-doped Ga2O3 polycrystalline samples were prepared by solid-phase sintering, and the effects of Zn doping on the optical properties of Ga2O3 were investigated. It is found that the introduced Zn ions disrupted the Ga-O bonds and formed ZnGa, altering the Ga-O vibration modes and causing a blue shift in the related Raman mode. From near-infrared to visible light-range was a transparent region for Zn-doped Ga2O3. The fundamental optical bandgap underwent a decrease with increasing Zn doping content, primarily due to the p-d orbital hybridization of the O 2p and Zn 3d orbitals causing an upward shift valence band maximum and band renormalization effect-induced band-tails. The recombination of electrons at donor levels (VO) and holes at acceptor levels (VGa or VO-VGa) gave rise to blue-green luminescence. Zn doping increased the concentration oxygen vacancies (VO), resulting in significant blue-green luminescence enhancement in Zn-doped Ga2O3. Additionally, Zn doping resulted in a noticeable reduction in the red luminescence of Ga2O3, which may be attributed to Zn doping suppressing nitrogen incorporation from the air during high-temperature preparation processes.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Research Progress on Graphene Oxide (GO)/Chitosan (CS) Multifunctional Nanocomposites for Drug Delivery
by
Yanqiu Hu, Lei Ma, Qi Shi, Jinghang Li, Yuguang Lv and Chaoyu Song
Inorganics 2025, 13(4), 98; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13040098 - 21 Mar 2025
Abstract
With the unprecedented progress of biomedical nanotechnology in the past few decades, traditional drug delivery systems (DDSs) have been incorporated into intelligent DDSs with stimulus responsive characteristics. Graphene oxide (GO) and Chitosan (CS) have excellent physical, chemical, mechanical, and optical properties, and their
[...] Read more.
With the unprecedented progress of biomedical nanotechnology in the past few decades, traditional drug delivery systems (DDSs) have been incorporated into intelligent DDSs with stimulus responsive characteristics. Graphene oxide (GO) and Chitosan (CS) have excellent physical, chemical, mechanical, and optical properties, and their synergistic effects have attracted widespread attention in the biomedical field. In this review, we focus on the physicochemical characteristics of GO, CS, and GO/CS composites, as well as the research progress of DDS types based on GO/CS.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Carbon Nanomaterials for Advanced Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
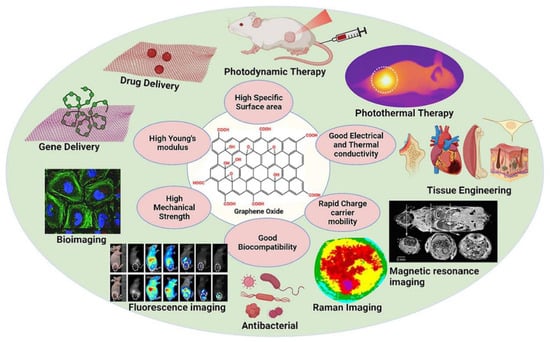
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Independent Acidic pH Reactivity of Non-Iron-Fenton Reaction Catalyzed by Copper-Based Nanoparticles for Fluorescent Dye Oxidation
by
Zakia H. Alhashem, Hasna Abdullah Alali, Shehab A. Mansour, Maha A. Tony and Ashraf H. Farha
Inorganics 2025, 13(3), 97; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030097 - 20 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The process of hydrogen peroxide decomposition, facilitated by copper oxide nanoparticles, produces reactive oxidants that possess the ability to oxidize multiple pollutants. CuO/Cu2O hybrid nanoparticles were successfully synthesized through a thermal decomposition route and applied as a heterogeneous catalytic oxidant for
[...] Read more.
The process of hydrogen peroxide decomposition, facilitated by copper oxide nanoparticles, produces reactive oxidants that possess the ability to oxidize multiple pollutants. CuO/Cu2O hybrid nanoparticles were successfully synthesized through a thermal decomposition route and applied as a heterogeneous catalytic oxidant for a fluorescent dye, namely Basic Violet 10 (BV10) dye. The microstructure and morphology of the prepared catalyst were evaluated via X-ray diffraction (XRD) and a field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), respectively. The produced nanoparticles (NPs) were induced through ultraviolet light as a green photodecomposition technology. The system parameters were investigated, and the optimal initial NP concentration, H2O2 concentration, and pH were assessed. The highest removal rate corresponding to 82% was achieved when 40 and 400 mg/L of NPs and H2O2 were introduced, respectively. The system could operate at various pH values, and the alkaline pH (8.0) was efficient in proceeding with the oxidation system that overcomes the limitation of the homogeneous acidic Fenton catalyst. The introduced catalyst demonstrated consistent sustainability, achieving a notable removal rate of 68% even after six consecutive cycles of use. This innovative technique’s accomplishment examines the feasibility of utilizing copper as a replacement for iron in the Fenton reaction, demonstrating efficacy over an extended pH range. Finally, the temperature effectiveness of the reaction showed that the reaction is exothermic in nature, working at a low energy barrier (20.4 kJ/mol) and following the pseudo-second-order kinetic model.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hollow-Structured Carbon-Coated CoxNiySe2 Assembled with Ultrasmall Nanoparticles for Enhanced Sodium-Ion Battery Performance
by
Chao Wang, Weijie Si and Xiongwu Kang
Inorganics 2025, 13(3), 96; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030096 - 20 Mar 2025
Abstract
Transition metal selenides are considered one of the most promising materials for sodium-ion battery anodes due to their excellent theoretical capacity. However, it remains challenging to suppress the volume variation and the resulted capacity decay during the charge–discharge process. Herein, hollow-structured CoNiSe2
[...] Read more.
Transition metal selenides are considered one of the most promising materials for sodium-ion battery anodes due to their excellent theoretical capacity. However, it remains challenging to suppress the volume variation and the resulted capacity decay during the charge–discharge process. Herein, hollow-structured CoNiSe2 dual transition metal selenides wrapped in a carbon shell (HS-CoxNiySe2@C) were deliberately designed and prepared through sequential coating of polyacrylonitrile (PAN), ion exchange of ZIF-67 with Ni2+ metal ions, and carbonization/selenization. The hollow structure was evidenced by transmission electron microscopy, and the crystalline structure was confirmed by X-ray diffraction. The ample internal space of HS-CoxNiySe2@C effectively accommodated volume expansion during the charge and discharge processes, and the large surface area enabled sufficient contact between the electrode and electrolyte and shortened the diffusion path of sodium ions for a feasible electrochemical reaction. The surface area and ionic conductivity of HS-CoxNiySe2@C were strongly dependent on the ratio of Co to Ni. The synergistic effect between Co and Ni enhanced the conductivity and electron mobility of HS-CoxNiySe2@C, thereby improving charge transfer efficiency. By taking into account the structural advantages and rational metal selenide ratios, significant improvements can be achieved in the cycling performance, rate performance, and overall electrochemical stability of sodium-ion batteries. The optimized HS-CoxNiySe2@C demonstrated excellent performance, and the reversible capacity remained at 334 mAh g−1 after 1000 cycles at a high current of 5.0 A g−1.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Inorganic Electrode Materials in High-Performance Energy Storage Devices)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Central Metal Ions (Dy, Er, Ni, and V) on the Structural and HSA-Binding Properties of 2-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde Semicarbazone Complexes
by
Violeta Jevtovic, Jelena M. Živković, Aleksandra A. Rakić, Aljazi Abdullah Alrashidi, Maha Awjan Alreshidi, Elham A. Alzahrani, Odeh A. O. Alshammari, Mostafa Aly Hussien and Dušan Dimić
Inorganics 2025, 13(3), 95; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030095 - 20 Mar 2025
Abstract
2-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde semicarbazone (HMBS) is a multidentate ligand with interesting coordination behavior that depends on the central metal ion and the overall complex geometry. In this contribution, the structural characteristics of five HMBS-containing complexes with different metal ions (Dy, Er, Ni, and V) were
[...] Read more.
2-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde semicarbazone (HMBS) is a multidentate ligand with interesting coordination behavior that depends on the central metal ion and the overall complex geometry. In this contribution, the structural characteristics of five HMBS-containing complexes with different metal ions (Dy, Er, Ni, and V) were investigated. Four binuclear and one mononuclear complex were selected from the Cambridge Structural Database. The crystallographic structures and intermolecular interactions in the solid state were analyzed, and the effect of central metal ions was elucidated. The different contributions of the most numerous contacts were explained by examining additional ligands in the structure. Density functional theory (DFT) optimizations were performed for the selected complexes, and the applicability of different computational methods was discussed. The Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules (QTAIMs) approach was employed to identify and quantify interactions in nickel and vanadium complexes, highlighting the role of weak intermolecular interactions between ligands in stabilizing the overall structure. Molecular docking studies of the interaction between these complexes and Human Serum Albumin (HSA) demonstrated that all compounds bind within the active pocket of the protein. The overall size and presence of aromatic rings emerged as key factors in the formation of stabilizing interactions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Metal Ion Research and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Studies on the Effect of Diamine Elongation in Copper(II) Complexes with NNO Tridentate Schiff Base Ligands
by
Chiara Canovi, Francesco Genua, Kevin D’Addazio, Lara Gigli, Alessandra Forni, Petr Michálek, Mauro Carcelli, Dominga Rogolino and Luca Rigamonti
Inorganics 2025, 13(3), 94; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030094 - 19 Mar 2025
Abstract
The copper(II) complexes of general formula [Cu(GL2H,H)(Cl)] (A4–A6, G = NO2, H and OMe, respectively), bearing NNO tridentate Schiff base ligands (GL2H,H)− derived from the mono-condensation of 1,3-diaminopropane
[...] Read more.
The copper(II) complexes of general formula [Cu(GL2H,H)(Cl)] (A4–A6, G = NO2, H and OMe, respectively), bearing NNO tridentate Schiff base ligands (GL2H,H)− derived from the mono-condensation of 1,3-diaminopropane and G-substituted salicylaldehydes, are here reported. The elongation of the diamine with one additional carbon atom with respect to the triad derived from ethylenediamine [Cu(GL1H,H)(Cl)] (A1–A3, G = NO2, H and OMe, respectively) led to different synthetic procedures, with the difficult isolation of A6 that could be obtained only in few crystals suitable for X-ray diffractions. Operating in acidic conditions to promote the coordination of chloride and expulsion of pyridine from the complex [Cu(GL2H,H)(py)](ClO4) (G = NO2) allows for obtaining A4. On the other hand, structural rearrangement occurs when G = H, yielding the dinuclear species [Cu2(μ-saltn)(HL2H,H)](ClO4)⋅0.5MeOH (D5⋅0.5MeOH) instead of the desired A5, which can be obtained by avoiding the use of HCl and operating in the excess of LiCl. Finally, A4 and A5 were investigated as cytotoxic agents against malignant (MDA-MB-231 and 22-Rv1) and healthy (HaCaT) cell lines, and the ability of the most promising A5 to be internalized and interact with cellular targets was studied.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue State-of-the-Art Inorganic Chemistry in Italy)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Novel 3-Ethoxysalicylaldehyde Lanthanide Complexes Obtained by Decomposition of Salen-Type Ligands
by
Paula Mediavilla, Antonio Ribeiro, Ángel Gutiérrez, Santiago Herrero and Mari Carmen Torralba
Inorganics 2025, 13(3), 93; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030093 - 19 Mar 2025
Abstract
Three new asymmetrically coordinated lanthanide derivatives based on the bicompartmental salen-type ligands N,N′-bis(3-ethoxysalicylidene)propylene-1,3-diamine (H2EtOsalpr) and 3-ethoxysalicylaldehyde (HEtvain) have been synthesized and structurally and photophysically characterized. All the compounds show dimeric structures of the
[...] Read more.
Three new asymmetrically coordinated lanthanide derivatives based on the bicompartmental salen-type ligands N,N′-bis(3-ethoxysalicylidene)propylene-1,3-diamine (H2EtOsalpr) and 3-ethoxysalicylaldehyde (HEtvain) have been synthesized and structurally and photophysically characterized. All the compounds show dimeric structures of the general formula [Ln(H2EtOsalpr)(NO3)2(Etvain)]2 (Ln = Nd, Eu, Dy), with each salen-type ligand bridging two lanthanide ions. The Etvain ligand comes from the H2EtOsalpr decomposition being coordinated to the corresponding lanthanide. The Nd(III) derivative shows fluorescence emission in the NIR region, but for the Eu(III) and Dy(III) compounds, only a broad band, attributed to the ligand emission, was observed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Coordination Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Employing Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Explore the Behavior of Diphenylalanine Dipeptides in Graphene-Based Nanocomposite Systems
by
Elena Markopoulou, Panagiotis Nikolakis, Gregory Savvakis and Anastassia N. Rissanou
Inorganics 2025, 13(3), 92; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030092 - 19 Mar 2025
Abstract
Utilizing all-atom molecular dynamics simulations, in the current study, we examine how three different graphene-based nanosheets (pristine graphene, graphene oxide and edge-functionalized graphene) impact the self-assembly mechanism of diphenylalanine dipeptides in aqueous solutions. By comparing the conformational properties and dynamics of diphenylalanine dipeptides
[...] Read more.
Utilizing all-atom molecular dynamics simulations, in the current study, we examine how three different graphene-based nanosheets (pristine graphene, graphene oxide and edge-functionalized graphene) impact the self-assembly mechanism of diphenylalanine dipeptides in aqueous solutions. By comparing the conformational properties and dynamics of diphenylalanine dipeptides in the presence of each nanosheet, we elucidate the effects of the existence of functional groups, their type, and their position on the formed nanostructures. We quantify the interaction energy between diphenylalanine dipeptides and the nanosheets, analyzing various energetic components, to gain insights into the driving forces for the assembly procedure in the nanocomposite systems. Dipeptides readily coat nanosheets due to their high surface affinity. Subsequent diphenylalanine self-assembly is determined by the nanofiller type: in the systems with graphene oxide and edge functionalized graphene, there is an increase of the interfacial layer thickness, while in the system with pristine graphene a structure extended on top of the coating layer is formed. Additionally, we monitor how dipeptides facilitate the dispersion of graphene-based nanosheets in aqueous solution. The findings of this work enhance our understanding of the interplay between diphenylalanine dipeptides and graphene-based nanosheets, paving the way for the rational design of novel materials with tailored properties for specific applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Carbon Nanomaterials for Advanced Technology)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
The Conversion Polymorphism of Perovskite Phases in the BiCrO3–BiFeO3 System
by
Alexei A. Belik
Inorganics 2025, 13(3), 91; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030091 - 18 Mar 2025
Abstract
Perovskite-type materials containing Bi3+ cations at A sites are interesting from the viewpoints of applications and fundamental science as the lone pair of Bi3+ cations often stabilizes polar, ferroelectric structures. This can be illustrated by a lot of discoveries of different
[...] Read more.
Perovskite-type materials containing Bi3+ cations at A sites are interesting from the viewpoints of applications and fundamental science as the lone pair of Bi3+ cations often stabilizes polar, ferroelectric structures. This can be illustrated by a lot of discoveries of different new functionalities in bulk and thin films of BiFeO3 and its derivatives. In this work, we investigated solid solutions of BiCr1−xFexO3 with 0.1 ≤ x ≤ 0.4 prepared by a high-pressure (HP) method and post-synthesis annealing at ambient pressure (AP). HP-BiCr1−xFexO3 modifications with 0.1 ≤ x ≤ 0.3 were mixtures of two phases with space groups C2/c and Pbam, and the amount of the C2/c phase decreased with increasing x. The amount of the C2/c phase was also significantly decreased in AP-BiCr1−xFexO3 modifications, and the C2/c phase almost disappeared in AP-BiCr1−xFexO3 with 0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.3. Fundamental, strong reflections of HP-BiCr1−xFexO3 and AP-BiCr1−xFexO3 were almost unchanged; on the other hand, weak superstructure reflections were different and showed clear signs of strong anisotropic broadening and incommensurate positions. These structural features prevented us from determining their room-temperature structures. On the other hand, HP-BiCr1−xFexO3 and AP-BiCr1−xFexO3 showed high-temperature structural phase transitions to the GdFeO3-type Pnma modification at Tsrt = 450 K (x = 0.1), Tsrt = 480 K (x = 0.2), Tsrt = 510 K (x = 0.3), and Tsrt = 546 K (x = 0.4). Crystal structures of the GdFeO3-type Pnma modifications of all the samples were investigated by synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction. Magnetic properties of HP-BiCr1−xFexO3 and AP-BiCr1−xFexO3 were quite close to each other (HP vs. AP), and the x = 0.2 samples demonstrated negative magnetization phenomena without signs of the exchange bias effect.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Photoelectric Research in Advanced Energy Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Cd(II)-Based Coordination Polymers and Supramolecular Complexes Containing Dianiline Chromophores: Synthesis, Crystal Structures, and Photoluminescence Properties
by
Nicoleta Craciun, Elena Melnic, Anatolii V. Siminel, Natalia V. Costriucova, Diana Chisca and Marina S. Fonari
Inorganics 2025, 13(3), 90; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030090 - 18 Mar 2025
Abstract
Five new coordination compounds that included three coordination polymers and two supramolecular complexes were obtained by reactions of different cadmium salts (tetrafluoroborate, nitrate, and perchlorate) with dianiline chromophores, 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane (ddpm), and 4,4′-diaminodiphenylethane (ddpe). The crystal structures were studied by single-crystal X-ray analysis. The
[...] Read more.
Five new coordination compounds that included three coordination polymers and two supramolecular complexes were obtained by reactions of different cadmium salts (tetrafluoroborate, nitrate, and perchlorate) with dianiline chromophores, 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane (ddpm), and 4,4′-diaminodiphenylethane (ddpe). The crystal structures were studied by single-crystal X-ray analysis. The coordination arrays with the ddpm chromophore included {[Cd(OH)(H2O)(ddpm)2](BF4)}n (1) as a one-dimensional (1D) coordination garland chain, {[Cd(NO3)(ddpm)2](H2O)(NO3)}n (2) as a two-dimensional (2D) coordination layer, and [Cd(bpy)2(ddpm)2](ddpm)(NO3)2 (3) as a supramolecular complex. The products with the ddpe chromophore were identified as {[Cd(phen)2(ddpe)](ClO4)2}n (4) in the form of a linear coordination chain and [Cd(phen)3](ClO4)2(ddpe)0.5(CH3CN)0.5 (5) as a supramolecular complex. The extension of coordination arrays in 1, 2, and 4 was achieved via dianiline ligands as bidentate linkers and additionally via bridging of nitrate anions in 2. The diversification of products became possible due to usage of 2,2′-bipyridine (bpy) and 1,10-phenanthroline (phen) as co-ligands forming the terminal corner fragments [Cd(bpy)2]2+, [Cd(phen)2]2+, and [Cd(phen)3]2+ in 3–5, respectively. The assembling of coordination entities occurred via the interplay of hydrogen bonds with the participation of amino groups, water molecules, and inorganic anions. Two dianilines were powerful luminophores in the crystalline phase, while the photoluminescence in 1–5 was considerably weaker than in the pure ddpm and ddpe luminophores and redistributed along the spectrum.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Coordination Chemistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
The Synthesis of NiY Zeolite via the Acid Hydrolysis of Ethyl Silicate and Its Catalytic Performance in the Degradation of Benzyl Phenyl Ethers
by
Bosen Zhou, Zhengbo Lai, Yuanyuan Li, Hualan Zhou, Ye Tian, Yibo Zhao and Ming Xia
Inorganics 2025, 13(3), 89; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030089 - 17 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The siliceous precursor was hydrolyzed from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) under acidic conditions, followed by the addition of sodium aluminate and sodium hydroxide. Y zeolite was subsequently obtained through hydrothermal crystallization under alkaline conditions. Key synthesis parameters, including reactant molar ratios, crystallization temperature, and time,
[...] Read more.
The siliceous precursor was hydrolyzed from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) under acidic conditions, followed by the addition of sodium aluminate and sodium hydroxide. Y zeolite was subsequently obtained through hydrothermal crystallization under alkaline conditions. Key synthesis parameters, including reactant molar ratios, crystallization temperature, and time, were systematically varied to optimize the synthesis conditions. The synthesized products were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), nitrogen adsorption analysis, and inductively coupled plasma (ICP) elemental analysis. Well-crystallized Y zeolite with a silica-alumina ratio (SAR) of 5.55 was successfully synthesized via TEOS hydrolysis catalyzed by sulfuric acid at a low crystallization temperature of 85 °C. The catalytic performance of benzyl phenyl ether, a lignin model compound, over NiY catalyst was evaluated in a high-pressure reactor. The results indicate that the catalytic efficiency of Y zeolite synthesized using TEOS as the silicon source under acidic hydrolysis conditions is significantly superior to Y zeolite prepared using alkaline silica sol as the silicon source.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
MoS2/MgAl-LDH Composites for the Photodegradation of Rhodamine B Dye
by
Jingjing Dai, Guofei Li, Yuanyuan Wang, Cancan Zhang, Hui Nan and Guijun Yang
Inorganics 2025, 13(3), 88; https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13030088 - 17 Mar 2025
Abstract
During the process of producing potassium fertilizer from salt lake resources, a large amount of waste liquid brine, rich in raw materials such as magnesium chloride, is generated. In this work, a MoS2/MgAl-LDH composite material was constructed using the secondary hydrothermal
[...] Read more.
During the process of producing potassium fertilizer from salt lake resources, a large amount of waste liquid brine, rich in raw materials such as magnesium chloride, is generated. In this work, a MoS2/MgAl-LDH composite material was constructed using the secondary hydrothermal technique. Characterizations including X-ray diffractometer (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) confirmed the distribution of MoS2 nanosheets on the surface of MgAl-LDH. Under full-spectrum irradiation, the degradation efficiency of Rhodamine B reached 85.5%, which was 69.2% higher than that of MgAl-LDH alone. The results from the electrochemical, UV-Vis, and XPS-VB tests indicate that the internal electric field accelerated the separation and transportation of charge carriers between MoS2 and MgAl-LDH. These findings demonstrate the great potential of MoS2/MgAl-LDH as a photocatalyst in the degradation of organic dyes, which will aid in the green recycling utilization of magnesium resources from salt lake by-products.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Photoelectric Research in Advanced Energy Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Inorganics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Chemistry, Molecules, IJMS, Biomolecules, Inorganics
Metal Ions in Health and Diseases: Current Progress and Future Challenges
Topic Editors: Massimiliano F. Peana, Carlo Santini, Maura PelleiDeadline: 31 May 2025
Topic in
Catalysts, Chemistry, Inorganics, Molbank, Molecules, Polymers
Heterocyclic Carbene Catalysis
Topic Editors: Sabine Berteina-Raboin, Thierry Besson, Patrick RollinDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Chemistry, Inorganics, IJMS, Pharmaceuticals
Natural Coumarin and Metal Complexes: Pharmacological Properties and Potential ApplicationsTopic Editors: Dušan Dimić, Edina Avdović, Dejan MilenkovićDeadline: 31 January 2026
Topic in
Atoms, Crystals, Molecules, Organics, Symmetry, Inorganics
Advances in Molecular Symmetry and Chirality Research
Topic Editors: Ralph N. Salvatore, Guzman Gil-RamirezDeadline: 31 March 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Inorganics
Revealing Reaction Mechanisms in Homogeneous Transition Metal Catalysis, 2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Axel Klein, S. Masoud Nabavizadeh, Fatemeh Niroomand HosseiniDeadline: 31 March 2025
Special Issue in
Inorganics
Development and Applications of Sterically Demanding Ligands in Main Group Chemistry
Guest Editor: Andreas StaschDeadline: 31 March 2025
Special Issue in
Inorganics
C–H Bond Activation by Transition Metal Complexes
Guest Editor: Francisco Núñez-ZarurDeadline: 31 March 2025
Special Issue in
Inorganics
Advanced Electrocatalysis Materials Design: Innovations and Applications
Guest Editor: Junxian LiuDeadline: 20 April 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Inorganics
Coordination Complexes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells (DSCs)
Collection Editor: Catherine Housecroft







